Understanding Different Qualification Frameworks: MEDDICC, BANT, GPCTBA/C&I, SPICED, FAINT, CHAMP, SCOTSMAN, and ANUM
When it comes to maximizing sales efficiency and ensuring that leads turn into customers, understanding different qualification frameworks is essential for sales teams. Numerous frameworks exist, each offering unique methodologies for qualifying leads, thus enabling sales professionals to prioritize their efforts effectively. In this post, we will explore various qualification frameworks: MEDDICC, BANT, GPCTBA/C&I, SPICED, FAINT, CHAMP, SCOTSMAN, and ANUM.
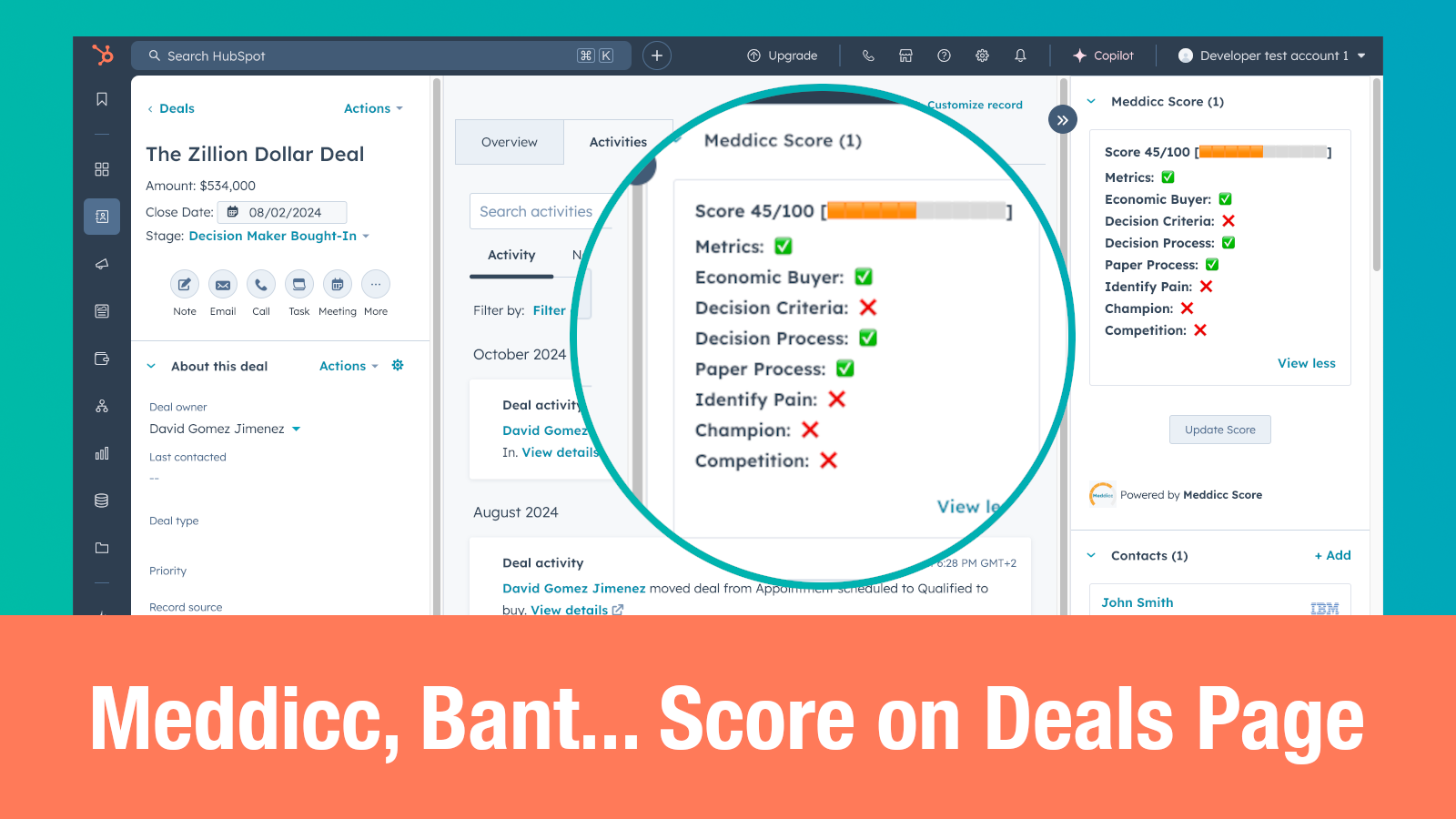
1. MEDDICC
MEDDICC stands for Metrics, Economic Buyer, Decision Criteria, Decision Process, Identify Pain, Champion, and Competition. This framework focuses on understanding the actual needs and issues facing the buyer, allowing sales teams to tailor their sales strategies accordingly.
Key Aspects:
- Metrics: Quantify the business impact of your solution.
- Economic Buyer: Identify who has the budget.
- Decision Criteria: Understand the factors influencing the buying decision.
- Decision Process: Map out the steps of the purchasing journey.
- Identify Pain: Discover the challenges the customer is facing.
- Champion: Find an internal advocate to help drive the deal.
- Competition: Analyze competitors and their offerings.
2. BANT
BANT – Budget, Authority, Need, and Timeline – is one of the classic frameworks in sales qualification. This straightforward approach helps sales professionals quickly determine whether a lead is worth pursuing.
Key Aspects:
- Budget: What can the prospect spend?
- Authority: Who makes the final decision?
- Need: Does the prospect have a problem that requires a solution?
- Timeline: When does the prospect plan to make a decision?
3. GPCTBA/C&I
GPCTBA/C&I stands for Goals, Plans, Challenges, Timeline, Budget, Authority, and Consequences & Implications. This more detailed approach digs deeper into the prospect’s motivations and broader context, enabling a more thorough qualification process.
Key Aspects:
- Goals: What does the prospect hope to achieve?
- Plans: What is their strategy for hitting these goals?
- Challenges: What obstacles are they facing?
- Timeline: The urgency behind their needs.
- Budget: Financial capabilities.
- Authority: Decision-makers involved.
- Consequences & Implications: Potential outcomes of not solving their issues.
4. SPICED
SPICED stands for Situation, Pain, Impact, Critical Event, and Decision Process. This framework encourages sales professionals to explore the specific context of the prospect’s situation and the urgency of their needs.
Key Aspects:
- Situation: Current status of the prospect.
- Pain: The problems they are experiencing.
- Impact: The consequences of their pain points.
- Critical Event: Significant deadlines or events driving urgency.
- Decision Process: Understanding the steps the prospect will take to decide.
5. FAINT
FAINT stands for Funds, Authority, Interest, Need, and Timing. This sales qualification framework is particularly useful for identifying lesser-known decision-makers or influencers within the buying process.
Key Aspects:
- Funds: Financial resources available.
- Authority: Decision-making power in the process.
- Interest: Level of interest in your offering.
- Need: Urgency of need for a solution.
- Timing: The timeframe for making a decision.
6. CHAMP
CHAMP is about Challenges, Authority, Money, and Prioritization. This framework flips the traditional qualification process on its head, starting with the prospect’s challenges to better align solutions.
Key Aspects:
- Challenges: What hurdles does the prospect face?
- Authority: Who can approve the purchase?
- Money: What is their spending capacity?
- Prioritization: How urgent is solving their challenges?
7. SCOTSMAN
SCOTSMAN is an acronym that means Solution, Competition, Originality, Timeframe, Size of opportunity, Money, Authority, and Need. This comprehensive framework allows sales professionals to conduct a thorough assessment across multiple dimensions.
Key Aspects:
- Solution: How well does your offer fit?
- Competition: Who else is vying for the same deal?
- Originality: What makes your solution stand out?
- Timeframe: Urgency for a resolution.
- Size of opportunity: Potential value of the deal.
- Money: Available budget.
- Authority: The decision-maker’s involvement.
- Need: Importance of the solution to the buyer.
8. ANUM
ANUM stands for Authority, Need, Urgency, and Money. This is a direct and no-frills qualification framework that helps sales professionals focus on key aspects that determine lead quality.
Key Aspects:
- Authority: Identify the decision-maker.
- Need: Understand the prospect’s requirements.
- Urgency: Assess how quickly they need a solution.
- Money: Verify budget availability.
Conclusion
Understanding these different qualification frameworks—MEDDICC, BANT, GPCTBA/C&I, SPICED, FAINT, CHAMP, SCOTSMAN, and ANUM—can significantly enhance your sales strategy. Each framework offers unique insights into the prospect’s needs and decision-making process, ultimately guiding you toward more effective sales interactions. By employing the right framework and adapting it to your context, you can ensure that your sales team operates efficiently and effectively.